Logto is an Auth0 alternative designed for modern apps and SaaS products. It offers both Cloud and Open-source services to help you quickly launch your identity and management (IAM) system. Enjoy authentication, authorization, and multi-tenant management all in one.
We recommend starting with a free development tenant on Logto Cloud. This allows you to explore all the features easily.
In this article, we will go through the steps to quickly build the Tencent sign-in experience (user authentication) with Go and Logto.
Prerequisites
- A running Logto instance. Check out the introduction page to get started.
- Basic knowledge of Go.
- A usable Tencent account.
Create an application in Logto
Logto is based on OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication and OAuth 2.0 authorization. It supports federated identity management across multiple applications, commonly called Single Sign-On (SSO).
To create your Traditional web application, simply follow these steps:
- Open the Logto Console. In the "Get started" section, click the "View all" link to open the application frameworks list. Alternatively, you can navigate to Logto Console > Applications, and click the "Create application" button.
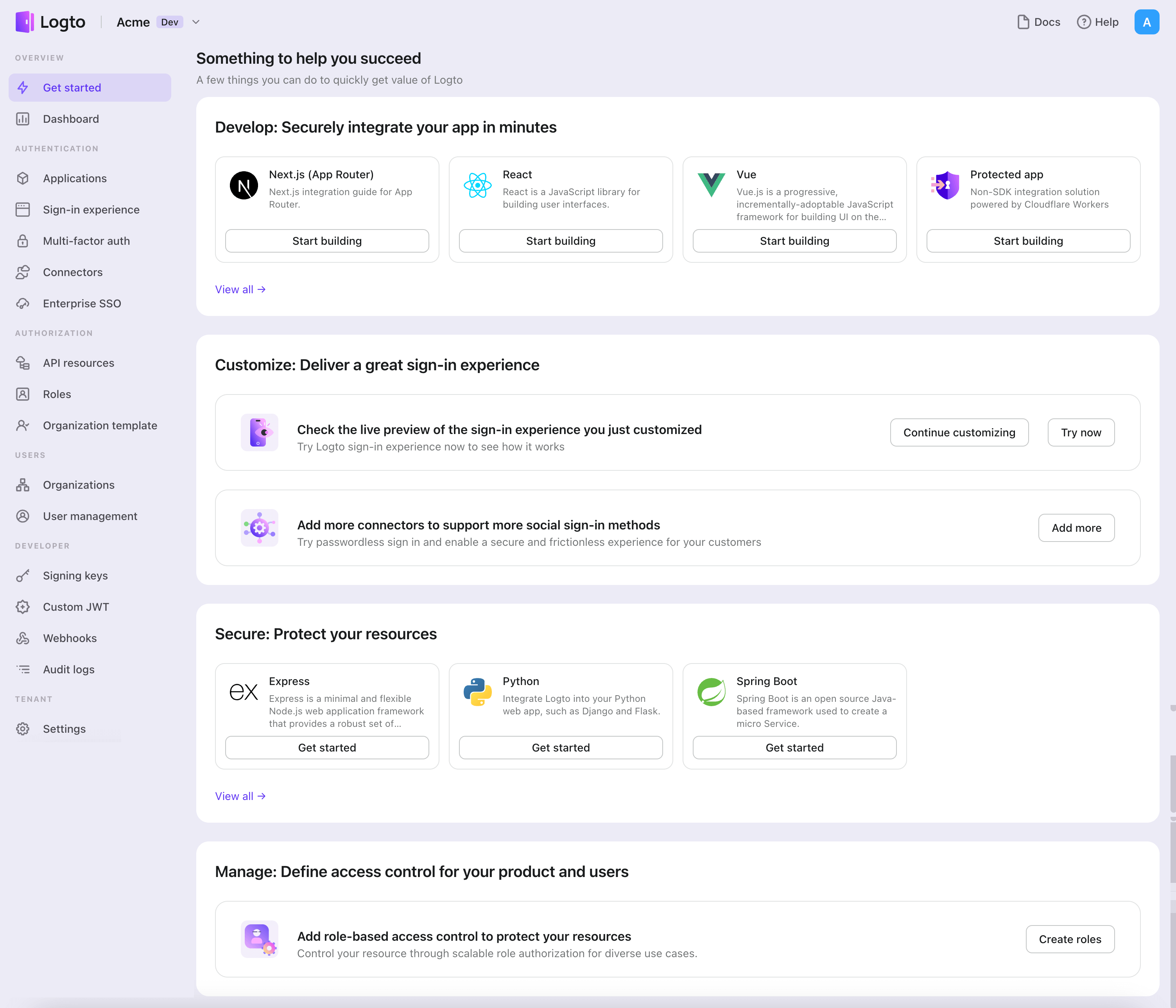
- In the opening modal, click the "Traditional web" section or filter all the available "Traditional web" frameworks using the quick filter checkboxes on the left. Click the "Go" framework card to start creating your application.
- Enter the application name, e.g., "Bookstore," and click "Create application".
🎉 Ta-da! You just created your first application in Logto. You'll see a congrats page which includes a detailed integration guide. Follow the guide to see what the experience will be in your application.
Integrate Go with Logto
- The following demonstration is built upon the Gin Web Framework. You may also integrate Logto into other frameworks by taking the same steps.
- The Go sample project is available on our Go SDK repo.
Installation
Execute in the project root directory:
go get github.com/logto-io/go
Add the github.com/logto-io/go/client package to your application code:
// main.go
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
// Add dependency
"github.com/logto-io/go/client"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(200, "Hello Logto!")
})
router.Run(":3000")
}
Create a session storage
In traditional web applications, the user authentication information will be stored in the user session.
Logto SDK provides a Storage interface, you can implement a Storage adapter based on your web framework so that the Logto SDK can store user authentication information in the session.
We do NOT recommend using cookie-based sessions, as user authentication information stored by Logto may exceed the cookie size limit. In this example, we use memory-based sessions. You can use Redis, MongoDB, and other technologies in production to store sessions as needed.
The Storage type in the Logto SDK is as follows:
package client
type Storage interface {
GetItem(key string) string
SetItem(key, value string)
}
We use github.com/gin-contrib/sessions middleware as an example to demonstrate this process.
Apply the middleware to the application, so that we can get the user session by the user request context in the route handler:
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-contrib/sessions"
"github.com/gin-contrib/sessions/memstore"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/logto-io/go/client"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
// We use memory-based session in this example
store := memstore.NewStore([]byte("your session secret"))
router.Use(sessions.Sessions("logto-session", store))
router.GET("/", func(ctx *gin.Context) {
// Get user session
session := sessions.Default(ctx)
// ...
ctx.String(200, "Hello Logto!")
})
router.Run(":3000")
}
Create a session_storage.go file, define a SessionStorage and implement the Logto SDK's Storage interfaces:
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-contrib/sessions"
)
type SessionStorage struct {
session sessions.Session
}
func (storage *SessionStorage) GetItem(key string) string {
value := storage.session.Get(key)
if value == nil {
return ""
}
return value.(string)
}
func (storage *SessionStorage) SetItem(key, value string) {
storage.session.Set(key, value)
storage.session.Save()
}
Now, in the route handler, you can create a session storage for Logto:
session := sessions.Default(ctx)
sessionStorage := &SessionStorage{session: session}
Init LogtoClient
First, create a Logto config:
func main() {
// ...
logtoConfig := &client.LogtoConfig{
Endpoint: "<your-logto-endpoint>", // E.g. http://localhost:3001
AppId: "<your-application-id>",
AppSecret: "<your-application-secret>",
}
// ...
}
You can find and copy "App Secret" from application details page in Admin Console:
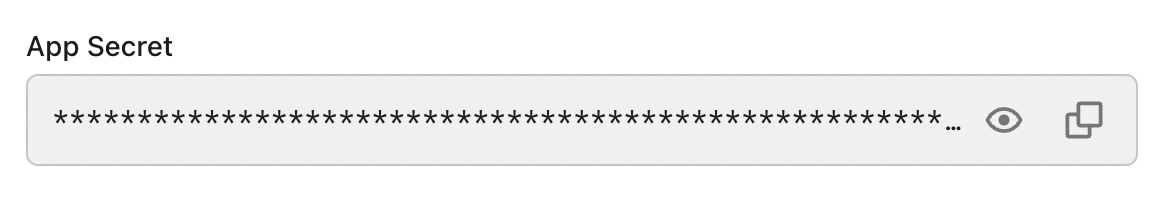
Then, you can create a LogtoClient for each user request with the Logto config above:
func main() {
// ...
router.GET("/", func(ctx *gin.Context) {
// Create LogtoClient
session := sessions.Default(ctx)
logtoClient := client.NewLogtoClient(
logtoConfig,
&SessionStorage{session: session},
)
// Use Logto to control the content of the home page
authState := "You are not logged in to this website. :("
if logtoClient.IsAuthenticated() {
authState = "You are logged in to this website! :)"
}
homePage := `<h1>Hello Logto</h1>` +
"<div>" + authState + "</div>"
ctx.Data(http.StatusOK, "text/html; charset=utf-8", []byte(homePage))
})
// ...
}
Implement sign-in route
After the redirect URI is configured, we add a sign-in route to handle the sign-in request and also add an sign-in link on the home page:
func main() {
// ...
// Add a link to perform a sign-in request on the home page
router.GET("/", func(ctx *gin.Context) {
// ...
homePage := `<h1>Hello Logto</h1>` +
"<div>" + authState + "</div>" +
// Add link
`<div><a href="/sign-in">Sign In</a></div>`
ctx.Data(http.StatusOK, "text/html; charset=utf-8", []byte(homePage))
})
// Add a route for handling sign-in requests
router.GET("/sign-in", func(ctx *gin.Context) {
session := sessions.Default(ctx)
logtoClient := client.NewLogtoClient(
logtoConfig,
&SessionStorage{session: session},
)
// The sign-in request is handled by Logto.
// The user will be redirected to the Redirect URI on signed in.
signInUri, err := logtoClient.SignIn("http://localhost:3000/callback")
if err != nil {
ctx.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, err.Error())
return
}
// Redirect the user to the Logto sign-in page.
ctx.Redirect(http.StatusTemporaryRedirect, signInUri)
})
// ...
}
Now, when your user visit http://localhost:3000/sign-in, the user will be redirected to the Logto sign-in page.
Implement the callback route
When the user signs in successfully on the Logto sign-in page, Logto will redirect the user to the Redirect URI.
Since the redirect URI is http://localhost:3000/callback, we add the /callback route to handle the callback after signing in.
func main() {
// ...
// Add a route for handling sign-in callback requests
router.GET("/callback", func(ctx *gin.Context) {
session := sessions.Default(ctx)
logtoClient := client.NewLogtoClient(
logtoConfig,
&SessionStorage{session: session},
)
// The sign-in callback request is handled by Logto
err := logtoClient.HandleSignInCallback(ctx.Request)
if err != nil {
ctx.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, err.Error())
return
}
// Jump to the page specified by the developer.
// This example takes the user back to the home page.
ctx.Redirect(http.StatusTemporaryRedirect, "/")
})
// ...
}
Implement sign-out route
Similar to the sign-in flow, when the user signs out, Logto will redirect the user to the post sign-out redirect URI.
Now, let's add the sign-out route to handle the sign-out request and also add a sign-out link on the home page:
func main() {
// ...
// Add a link to perform a sign-out request on the home page
router.GET("/", func(ctx *gin.Context) {
// ...
homePage := `<h1>Hello Logto</h1>` +
"<div>" + authState + "</div>" +
`<div><a href="/sign-in">Sign In</a></div>` +
// Add link
`<div><a href="/sign-out">Sign Out</a></div>`
ctx.Data(http.StatusOK, "text/html; charset=utf-8", []byte(homePage))
})
// Add a route for handling signing out requests
router.GET("/sign-out", func(ctx *gin.Context) {
session := sessions.Default(ctx)
logtoClient := client.NewLogtoClient(
logtoConfig,
&SessionStorage{session: session},
)
// The sign-out request is handled by Logto.
// The user will be redirected to the Post Sign-out Redirect URI on signed out.
signOutUri, signOutErr := logtoClient.SignOut("http://localhost:3000")
if signOutErr != nil {
ctx.String(http.StatusOK, signOutErr.Error())
return
}
ctx.Redirect(http.StatusTemporaryRedirect, signOutUri)
})
// ...
}
After the user makes a signing-out request, Logto will clear all user authentication information in the session.
Checkpoint: Test your application
Now, you can test your application:
- Run your application, you will see the sign-in button.
- Click the sign-in button, the SDK will init the sign-in process and redirect you to the Logto sign-in page.
- After you signed in, you will be redirected back to your application and see the sign-out button.
- Click the sign-out button to clear token storage and sign out.
Add Tencent connector
SMS connector is a method used to send one-time passwords (OTPs) for authentication. It enables Phone number verification to support passwordless authentication, including SMS-based registration, sign-in, two-factor authentication (2FA), and account recovery. You can easily connect Tencent as your SMS provider. With the Logto SMS connector, you can set this up in just a few minutes.
To add a SMS connector, simply follow these steps:
- Navigate to Console > Connector > Email and SMS connectors.
- To add a new SMS connector, click the "Set up" button and select "Tencent".
- Review the README documentation for your selected provider.
- Complete the configuration fields in the "Parameter Configuration" section.
- Customize the SMS template using the JSON editor.
- Test your configuration by sending a verification code to your Phone number.
If you are following the in-place Connector guide, you can skip the next section.
Set up Tencent SMS connector
Create an Tencent Cloud account
Go to the Tencent Cloud website and register your account if you don't have one.
Enable and Configure Tencent Cloud SMS
- Sign-in with your account at the Tencent Cloud website and go to the SMS service console page.
- Click the “Free Trial” (免费试用) button on the SMS service page and follow the setup steps.
- Agree to the “Terms of SMS Service Activation” (短信开通服务条款) and click “Activate Service” (开通服务) to proceed.
- On the “SMS Console Overview” (短信服务控制台概览), choose “Domestic Messages”(国内消息) or “International/Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan Messages”(国际/港澳台消息) from the sidebar based on your needs.
- Add a signature and template for SMS messages. Note:
- When adding a “Signature” (签名), select “Verification Code” (验证码) under the "Applicable Scenarios" (模版类型) field.
- When adding a template, choose “Verification Code” as the template type.
- Include a placeholder
{1}in the template content, which will be replaced by a randomly generated code. - Templates with multiple placeholders are not supported. Use or create a single-placeholder template.
- Submit the signature and template for approval. After submission:
- Wait for them to take effect.
- Test SMS can be sent from the “SMS Console Overview” (短信服务控制台概览). Approved signatures and templates can be used directly for testing, or use the testing templates provided if they are still under review.
- Ensure your account has sufficient balance for testing and pre-register the test phone number to receive SMS successfully.
For detailed guidance, click the “Getting Started Guide” (新手配置指引) tab in the SMS Console Overview.
Compose the connector JSON
- Go to the “SMS Console Overview” and hover over your avatar in the top-right corner. Navigate to “Access Management > Access Keys > API Keys” to generate your
AccessKey IDandAccessKey Secretafter completing security verification. Please keep them properly. - From the “Domestic Messages” (国内消息) or “International/Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan Messages” (国际/港澳台消息) tab, retrieve the “Signature Name” (签名名称) and “Template Code” (模版 CODCE).
- For testing templates, check the “Getting Started” (快速开始) tab under "Test-Exclusive Templates" (测试专用签名模版).
- Configure the Tencent Cloud SMS Connector with the following fields:
accessKeyIdandaccessKeySecret: Use the credentials from step 1.signName: The signature name obtained in step 2. This applies to all templates.- Add multiple templates for different scenarios if needed. Example for a single template:
templateCode: Retrieved from the “Template Code” in step 2.usageType: Specify one ofRegister,SignIn,ForgotPassword, orGenericfor different scenarios (Logto-specific property).- Ensure templates are configured for all four scenarios to complete the flow.
sdkAppId: Found in “Application Management” (应用管理).region: Specify the supported region from the “Sending Documentation” (发送文档).
Test Tencent Cloud SMS connector
You can type in a phone number and click on "Send" to see whether the settings can work before "Save and Done".
That's it. Don't forget to Enable connector in sign-in experience.
Config types
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| accessKeyId | string |
| accessKeySecret | string |
| signName | string |
| region | string |
| sdkAppId | string |
| templates | Template[] |
| Template Properties | Type | Enum values |
|---|---|---|
| templateCode | string | N/A |
| usageType | enum string | 'Register' | 'SignIn' | 'ForgotPassword' | 'Generic' |
Save your configuration
Double check you have filled out necessary values in the Logto connector configuration area. Click "Save and Done" (or "Save changes") and the Tencent connector should be available now.
Enable Tencent connector in Sign-in Experience
Once you create a connector successfully, you can enable phone number-based passwordless login and registration.
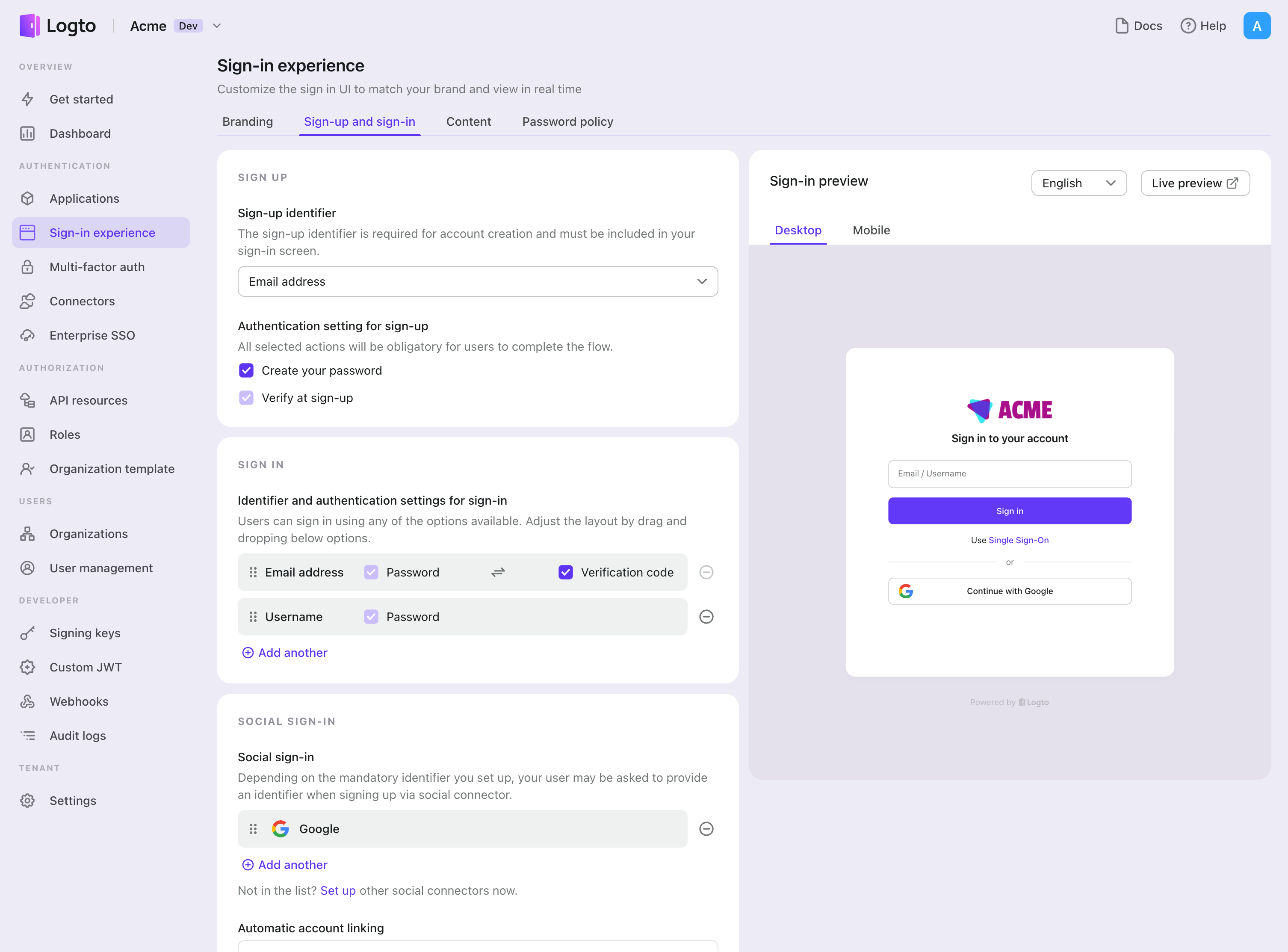
- Navigate to Console > Sign-in experience > Sign-up and sign-in.
- Set up sign-up methods (Optional):
- Select "Phone number" or "Email or phone number" as the sign-up identifier.
- "Verify at sign-up" is forced to be enabled. You can also enable "Create a password" on registration.
- Set up sign-in methods:
- Select Phone number as one of sign-in identifiers. You can provide multiple available identifiers (email, phone number, and username).
- Select "Verification code" and / or "Password" as the authentication factor.
- Click "Save changes" and test it in "Live preview".
In addition to registration and login via OTPs, you can also have password recovery and -based security verification enabled, as well as linking Phone number to profile. See End-user flows for more details.
Testing and Validation
Return to your Go app. You should now be able to sign in with Tencent. Enjoy!
Further readings
End-user flows: Logto provides a out-of-the-box authentication flows including MFA and enterprise SSO, along with powerful APIs for flexible implementation of account settings, security verification, and multi-tenant experience.
Authorization: Authorization defines the actions a user can do or resources they can access after being authenticated. Explore how to protect your API for native and single-page applications and implement Role-based Access Control (RBAC).
Organizations: Particularly effective in multi-tenant SaaS and B2B apps, the organization feature enable tenant creation, member management, organization-level RBAC, and just-in-time-provisioning.
Customer IAM series Our serial blog posts about Customer (or Consumer) Identity and Access Management, from 101 to advanced topics and beyond.